Acarbose API
49
05
Salvavidas Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd is a leading supplier Manufacturer and exporter of Acarbose API.
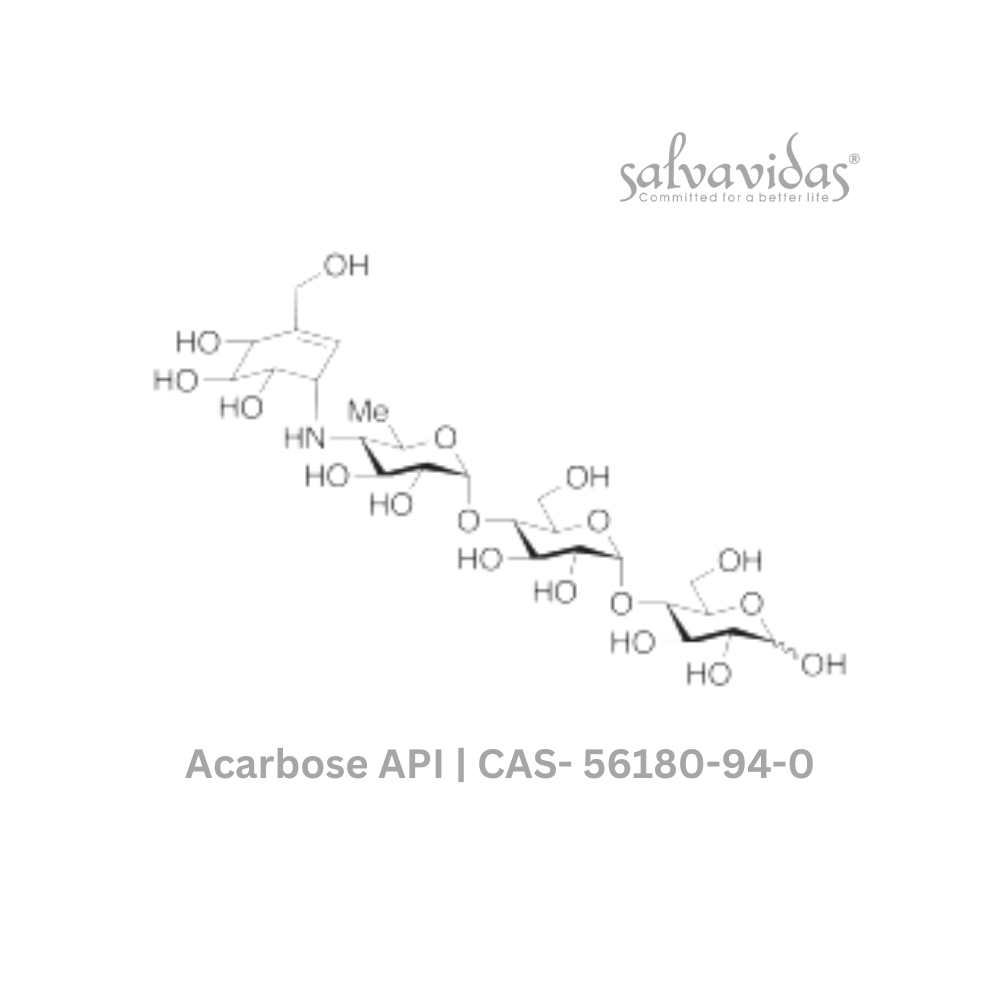
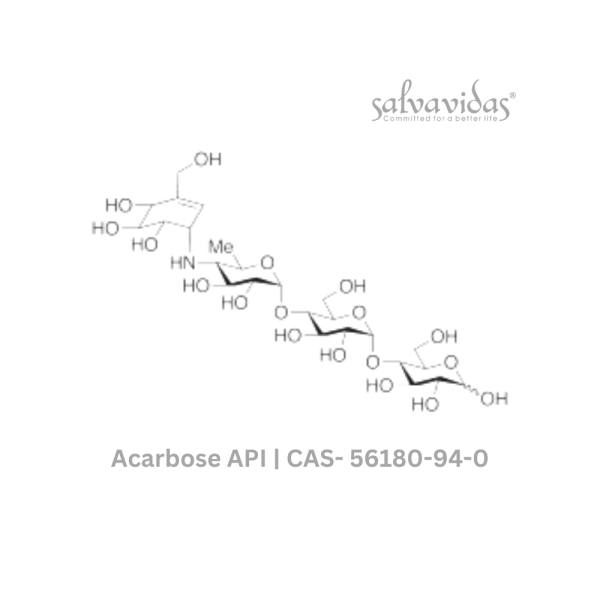
Acarbose API CAS 56180-94-0
A complex oligosaccharide called acarbose slows down the digestion of consumed carbs, causing a lesser increase in blood glucose levels after meals. Acarbose API lowers levels of glycosylated hemoglobin in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus as a result of lowering plasma glucose. Levels of glycosylated hemoglobin, which are a measure of systemic non-enzymatic protein glycosylation, depend on the average blood glucose level throughout time. Acarbose API does not increase insulin secretion as sulfonylureas do.
Acarbose Dose antihyperglycemic effect is caused by a competitive, reversible suppression of intestinal alpha-glucoside hydrolase enzymes that are membrane-bound and pancreatic alpha-amylase. The membrane-bound intestinal alpha-glucosidases hydrolyze oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and disaccharides to glucose and other monosaccharides in the brush border of the small intestine, while pancreatic alpha-amylase hydrolyzes complex starches to oligosaccharides in the lumen of the small intestine. This enzyme inhibition in diabetic patients delays the absorption of glucose and lowers postprandial hyperglycemia.
Acarbose API’s ability to improve glycemic control when combined with sulfonylureas, insulin, or metformin is additive because of its unique method of action. Acarbose also lessens the impact of sulfonylureas’ insulinotropic and weight-increasing actions.
Since acarbose has little inhibitory effect against lactase, it is not anticipated that it would cause lactose intolerance.
* Products will not be offered for sale in countries where valid Patents are in force.
* It is the responsibility of the buyer to comply with the above.
Related products
-

Piroxicam
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Bupropion Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

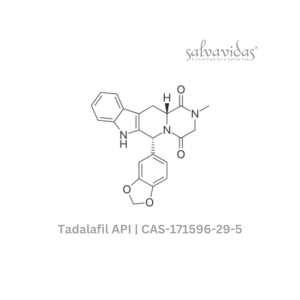
Tadalafil API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

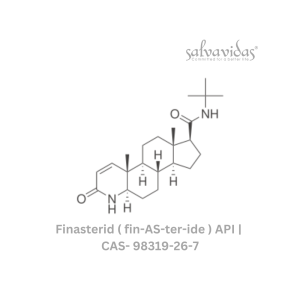
Finasterid ( fin-AS-ter-ide )
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

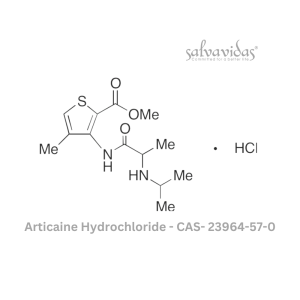
Articaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

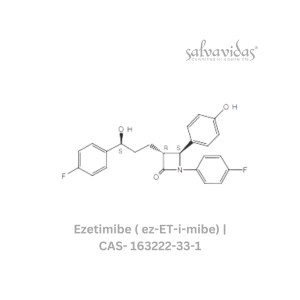
Ezetimibe ( ez-ET-i-mibe)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

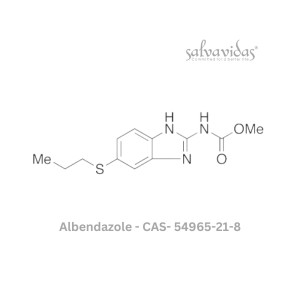
Albendazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

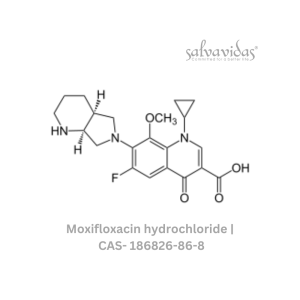
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

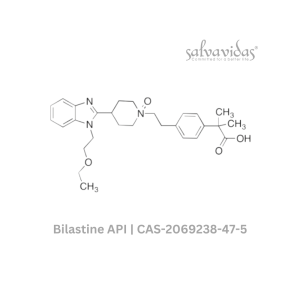
Bilastine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

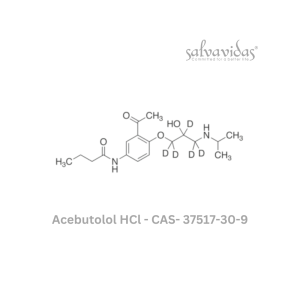
Acebutolol hcl
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

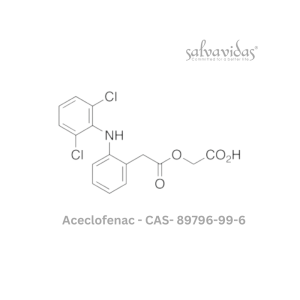
Aceclofenac
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

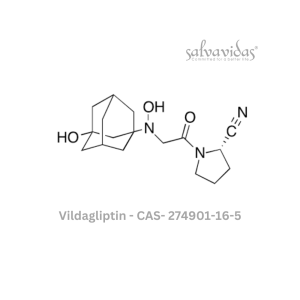
Vildagliptin API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

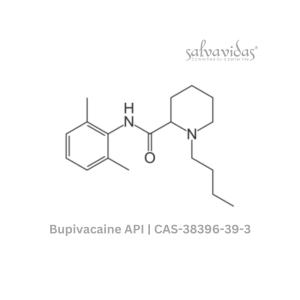
Bupivacaine API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

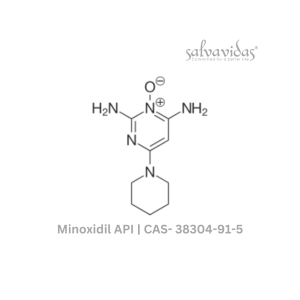
Minoxidil API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

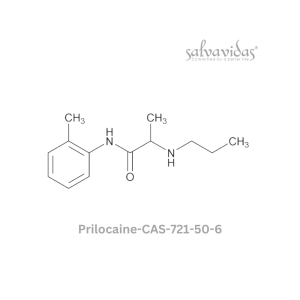
Prilocaine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

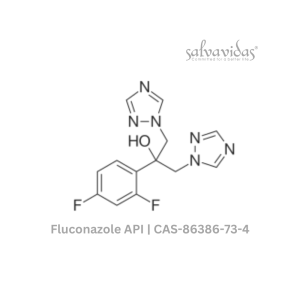
Fluconazole API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

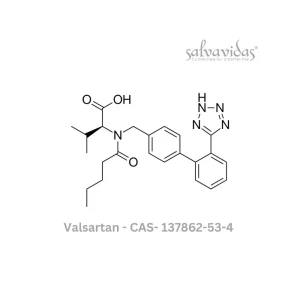
Valsartan API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

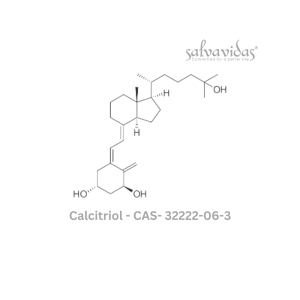
Calcitriol API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Rivaroxaban
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Prilocaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Acephylline
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Itraconazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

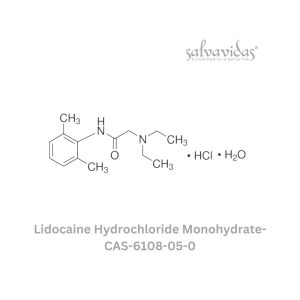
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Monohydrate
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

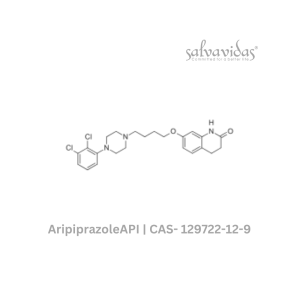
Aripiprazole (CAS 129722-12-9)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

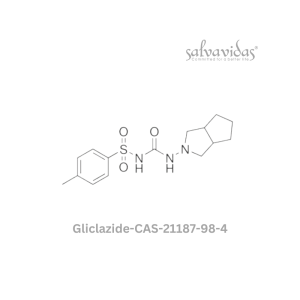
Gliclazide
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

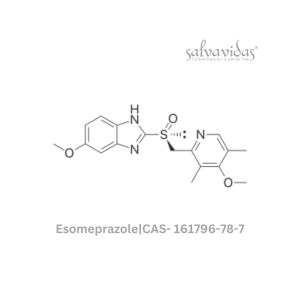
Esomeprazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Nebivolol HCL
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Pregabalin
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Molnupiravir API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Lidocaine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

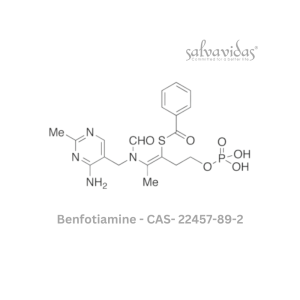
Benfotiamine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

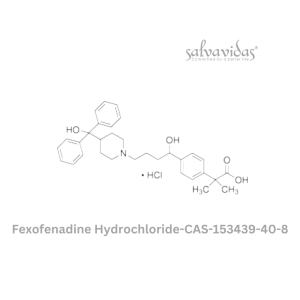
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

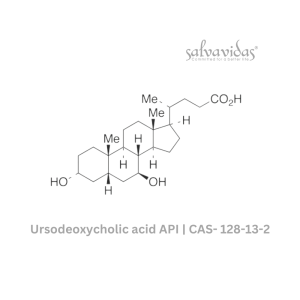
Ursodeoxycholic acid
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

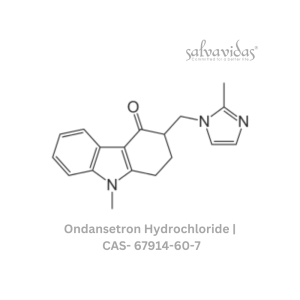
Ondansetron Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

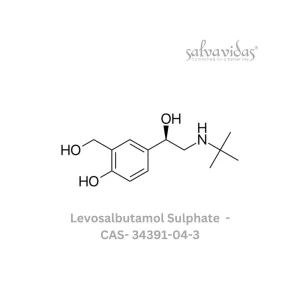
levosalbutamol sulphate API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

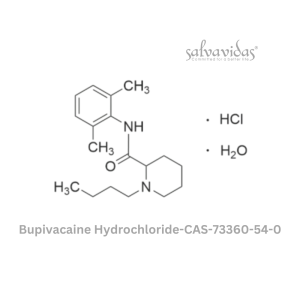
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

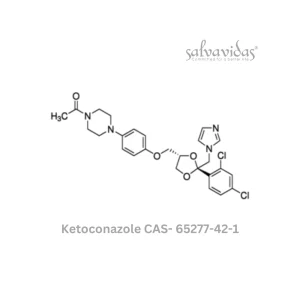
Ketoconazole API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

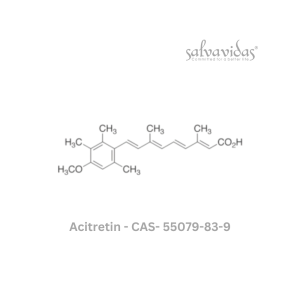
Acitretin
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

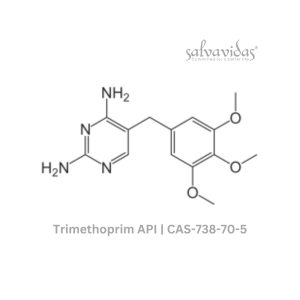
Trimethoprim API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

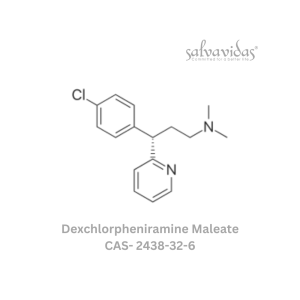
Dexchlorpheniramine Maleate
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

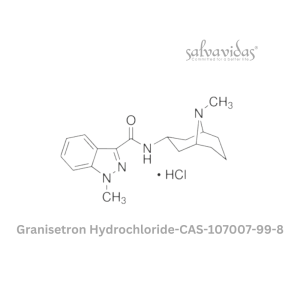
Granisetron Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

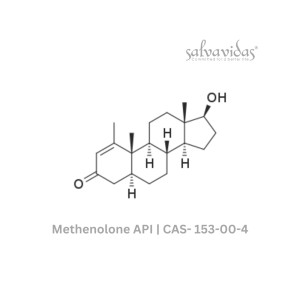
Methenolone
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

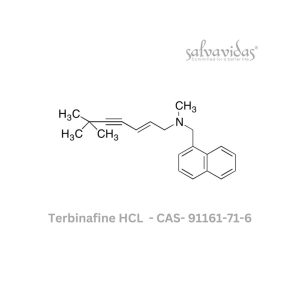
Terbinafine HCL
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

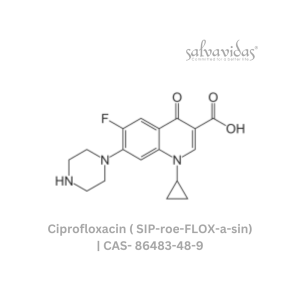
Ciprofloxacin ( SIP-roe-FLOX-a-sin)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

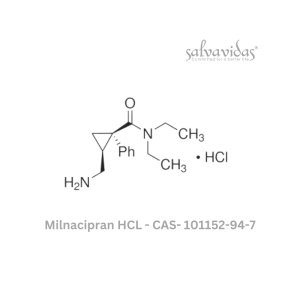
Milnacipran HCL API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

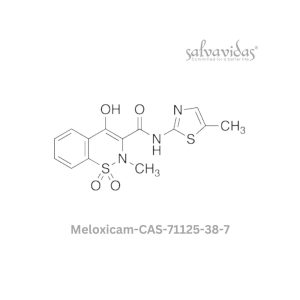
Meloxicam
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

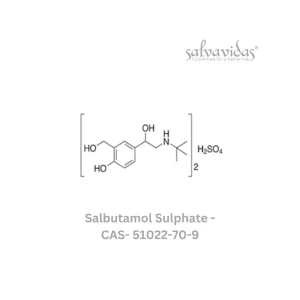
Salbutamol Sulphate API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

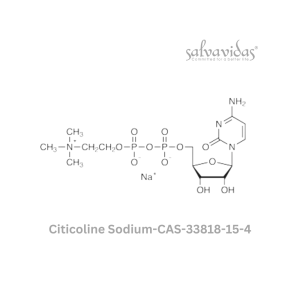
Citicoline Sodium
Rated 0 out of 5Read more
| Generic Name : | Acarbose API |
|---|---|
| CAS Number : | 56180-94-0 |
| Grade : | IP/BP/USP |
| Packing Type : | Drum |
| Therapeutic use : | Enzyme Inhibitors; Hypoglycemic Agents |
| Product MOQ : | 1 kg |
Product Inquiry Form
Your details will not be published
Related products
-

Ciprofloxacin ( SIP-roe-FLOX-a-sin)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Rivaroxaban
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Vildagliptin API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Aceclofenac
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Itraconazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Ursodeoxycholic acid
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Albendazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Methenolone
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Aripiprazole (CAS 129722-12-9)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Nebivolol HCL
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Trimethoprim API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Calcitriol API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Ezetimibe ( ez-ET-i-mibe)
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Bilastine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Pregabalin
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Fluconazole API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Citicoline Sodium
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Minoxidil API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Meloxicam
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Molnupiravir API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Prilocaine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Ondansetron Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

levosalbutamol sulphate API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Valsartan API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Lidocaine Hydrochloride Monohydrate
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Prilocaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Piroxicam
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Acitretin
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Acephylline
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Acebutolol hcl
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Dexchlorpheniramine Maleate
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Salbutamol Sulphate API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Benfotiamine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Milnacipran HCL API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Lidocaine
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Ketoconazole API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Terbinafine HCL
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Bupropion Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Gliclazide
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Tadalafil API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Finasterid ( fin-AS-ter-ide )
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Esomeprazole
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Bupivacaine API
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Articaine Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more -

Granisetron Hydrochloride
Rated 0 out of 5Read more